Water hardness is a common condition of tap water caused by a high content of dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium salts. This property of the liquid leads to a host of household problems: limescale in kettles, a chalky white residue on sinks, streaks on dishes, and a rainbow-like film on tea. Understanding your water hardness level is the first step to solving these issues.
There are two main types of hardness: temporary and permanent. Temporary hardness is easily removed by boiling, while permanent hardness is not. The scale in your kettle is the result of temporary hardness; when heated, calcium and magnesium compounds form an insoluble precipitate.
Ultimately, hard water undermines your household budget and, in some cases, can even influence your health. Therefore, learning how to find out water hardness and softening it is highly advisable.
The source of your water is the key factor. In some areas, water is naturally soft, while in others, it's very hard. The more limestone in the soil, the higher the water hardness.
Municipal water treatment plants typically do not focus on softening, but achieving soft water at home is a solvable task for any apartment or house owner. You just need to know the right method.
The value of water hardness is the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions. The international system recommends measuring in moles per cubic meter, but in practice, more convenient units are used.
The standard unit is degrees of hardness (°H or °dH), which is equal to milligram-equivalents per liter (mg-eq/l).
| Type of Water | Hardness, mg-ekv/l | Degrees, dH |
|---|---|---|
| Very Soft | < 1,5 | 0–4° |
| Soft | 1,5–3,0 | 5–8° |
| Medium Hardness | 3,0–8,0 | 9–12° |
| Hard | 8,0–12,0 | 13–22° |
| Very Hard | > 12,0 | 23–34° |
Drinking water hardness is divided into 3 categories:
The standard for tap water hardness should not exceed 7 mg-eq/l. However, the optimal level for drinking water is considered to be up to 2 °H, as it provides a safe amount of minerals without causing problems.
In practice, even medium hardness causes noticeable discomfort. A level of 4–5 °H will make itself known: it will leave scale in the kettle, a film on beverages, limescale on the sink, and will clog faucet aerators and showerheads.
Calcium salts in water are the primary "culprits" of its hardness. Technically, hardness salts also include magnesium and iron salts, but their amount is usually insignificant. It is precisely calcium that provokes limescale deposits. Therefore, the question "how to detect calcium" is essentially the same as asking how to determine overall water hardness.
There are several important reasons to measure the exact value:

The best way to know the exact composition of your water is through a laboratory analysis. This method provides the most accurate data not only on hardness but also on iron, nitrates, pesticides, hydrogen sulfide, and other impurities. This is especially important for household wells and when selecting a comprehensive water filter system.
If you use municipal tap water, you can often find the data for your region on your local water utility's website.
If you want to conduct an engaging experiment and research the hardness at home yourself, there are also opportunities for that.
Special test strips are sold in pet stores (for aquarium use) or stores selling coffee machines and appliances. The paper is coated with a reagent that changes color upon contact with water. The intensity of the color indicates the concentration.
The main drawback of this technique is its lower accuracy and the need to check the color against a provided chart, which can be subjective.
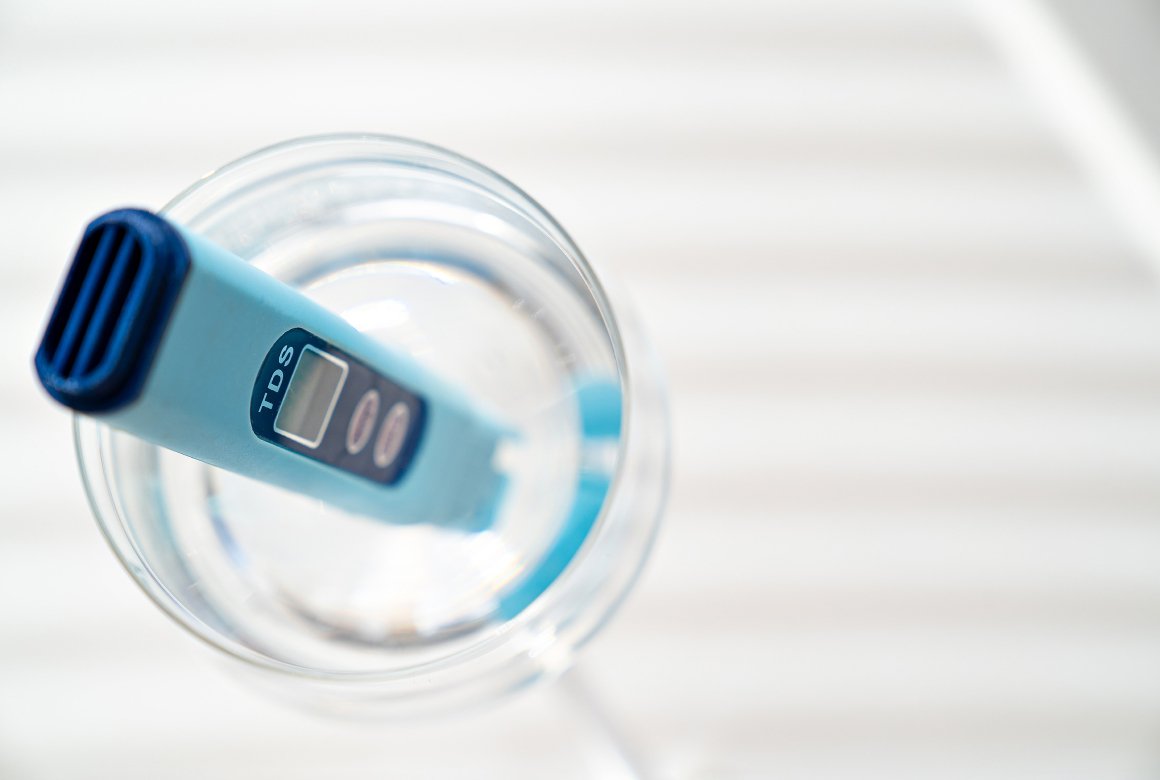
It is a common mistake to use a TDS meter for measuring water hardness. This device measures the electrical conductivity of water, which is influenced by all dissolved ions, not just calcium and magnesium. For example, if you add table salt to distilled water, the TDS meter will show a high value, indicating high mineral content, but the water will still be soft in terms of hardness. Therefore, a TDS meter is not a reliable means for this measurement.
To protect your expensive appliance from breakdown, it needs to be 'fed' with high-quality, soft water.
The method for determining water hardness for a dishwasher is exactly the same as for general purposes: it can be done in a laboratory, or at home — but in the latter case, the results will be very approximate, as we warned above.
The most effective water purification method for an apartment is the "mission" of a reverse osmosis filter. With this system, you can almost "skip" the water analysis: its special membrane completely removes hardness and any harmful impurities, including heavy metals, nitrates, and nitrites.
If a reverse osmosis filter is not suitable for you and your water is not too hard (up to 4–5 mg-eq/l), you can choose a sorption filter with an ion-exchange softening cartridge. However, it's important to know that the softening module will need to be periodically regenerated with ordinary table salt. The more hardness salts in the water, the more frequently regeneration is required. You can identify a softening module in Aquaphor filters by the "H" mark in the model name.
RO-101S: provides absolute protection against any harmful impurities. The quality is equivalent to bottled water. Ideal for allergy sufferers and newborns.
ECO H Pro: a system for deep purification and softening with absolute antibacterial protection.
AQUAPHOR S800: effectively softens water and removes high concentrations of iron and manganese.
For water treatment in cottages, comprehensive water softening and filtration systems are necessary, such as the AQUAPHOR S550, S800 or S1000 (they differ in productivity). Thanks to their design and principle of operation, the S-series softeners from AQUAPHOR are much more effective than other similar systems. They use twice less salt and five times less water for maintenance.
Important: If your water source is a well or borehole, the water must first be sent to a laboratory for analysis. After all, in addition to hardness salts, there may be other, more dangerous impurities.
A correctly selected filter will help you forget about hard water problems. The key is to first measure its hardness to choose the right model. AQUAPHOR specialists will always help and advise you.